Sperry Corporation and Sperry Marine
The history of the Sperry Corporation is the story of technological innovation and the application of that technology to everyday, real world uses. The history of Sperry Gyroscope and its successor companies and that heritage that ultimately resides with Sperry Marine, is one that follows the basic tenets of the founder himself. E.A. Sperry was first and foremost an engineer of the highest caliber. But to his credit, he was also as equally talented as an entrepreneur. The Sperry Marine of today continues to embody those two attributes.
Sperry Gyroscope Company
Sperry Marine has its origins in the Sperry Gyroscope Company. Named after its founder, Elmer A. Sperry, and established on April 19, 1910, with no outside financing, no products, no employees, but with an "unquenchable enthusiasm". Sperry Gyroscope grew to be a multinational technological powerhouse known the world over. This is an abbreviated history of the Sperry Marine Company and its evolution from those early beginnings to the company that today is recognized as one of the preeminent marine technology and manufacturing companies in the world.

Elmer Ambrose Sperry
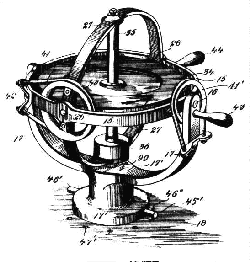
The Gyrocompass and Sperry Gyroscope
C.A. Bohnenberger is generally credited with the first recorded construction of a gyroscope in 1810. L. Foucault (of Pendulum fame) first conceived of the gyro as an inertial reference in 1851. In 1890, one other event was to set the stage for the practical application of the gyrocompass; the development of the first electrically driven gyroscope by G.M. Hopkins. Thus it was that in the last decade of the 19th century, the stage was set for the application of the gyroscope to real world problems. These were quick in coming; three things drove the transformation of the gyroscope from a child's toy, or inventor's curiosa to that of a usable technology. These were the increasing use of steel in ships which then brought about the second need; to overcome the unreliability of the magnetic compass within a steel ship, and finally, the great powers were preparing to conduct underwater warfare - in steel hull ships. In this age of the Edison's, Bell's and Wright brothers, two further inventors, one on either side of the Atlantic, sought solutions to these problems.
Dr. H. Anschutz of Germany and Elmer Sperry both built on the properties of the gyroscope; stability and precession. A gyroscope will always point to a fixed point in space if left undisturbed. If force is exerted upon it, it will react at right angles to the force applied. This characteristic of a gyro combined with other elements of precession, pendulocity and damping will allow the gyro to settle toward true north. In 1908 Dr. Anschutz patented the first north seeking gyrocompass with the United Kingdom's Patent Office (Patent Number 10382/08). That same year, Elmer Sperry invented and introduced the first ballistic gyrocompass, which included vertical damping (his device was subsequently patented with the British in 1911 - Patent Number 15669/11). Both of these first devices were of the single pendulum type.
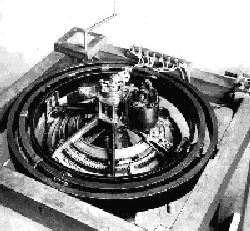
Unit 100 and the First World War
In 1911 the first Sperry gyro (Unit Number 100 shown at right) was installed aboard the Old Dominion Line PRINCESS ANNE for a trial run from New York to Hampton Roads, Virginia. Upon completing this trial the unit was brought back to New York and installed aboard the U.S.S. DELAWARE. Trials aboard the DELAWARE were launched starting on August 18, 1911. From this trial aboard the DELAWARE an order for four systems soon arrived from the U.S. Navy and Sperry Gyroscope was a reality. The first serially produced unit, Serial Number 101, was installed aboard the U.S.S. UTAH on November 13, 1911.
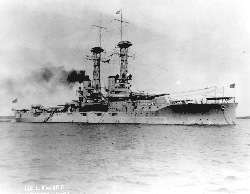 U.S.S. DELAWARE U.S.S. DELAWARE
Upon successful installation and trial aboard the U.S.S. DELAWARE, shown to the left, the ship was sent to participate in the coronation of King George V of England. During her absence, Elmer Sperry arranged with the Bureau of Ordnance of the U.S. Navy to have another of his gyros installed aboard the U.S.S. DRAYTON. From this trial resulted the Repeater Compass and the target bearing pointer. During this period Admiral Joseph Strauss, Chief of Naval Ordnance, encouraged Sperry to examine the basic fundamentals of fire control problems faced by ship borne long range guns. From this beginning, the Sperry Gyroscope Company developed the first full gun battery fire control system, which were ultimately placed aboard every U.S. battleship during World War I (some 30 ships). During the War another famous Sperry product was developed; "Metal Mike" or the first gyro pilot system for ship's steering. In fact, the impact of the war on Sperry Gyro was tremendous. Not only had the U.S. purchased the Sperry gyrocompass, but so had the British, French, Italian and Russian navies. For a variety of reasons, not the least of which was the impending war in Europe, Sperry Gyroscope Company Limited was formed in the U.K. in 1913. Production in Britain of the Sperry MK1 Gyrocompass commenced shortly thereafter. (Note: Production of Sperry gyro's continued in the U.K. until the late 1970's when the company was sold to British Aerospace.)
Gyro stabilizer system
Also about this time Sperry provided the Navy with its first gyro stabilizer system. The gyro weighed five tons and was installed aboard the U.S.S. WORDEN, a small destroyer of 700 tons. The gyro kept the ship from rolling as it was designed to do. From this successful demonstration of the gyro stabilizer, the U.S. Navy ordered a second system that was installed aboard the submarine E4. World War One started soon thereafter and further orders were put "on ice" as it was not considered an "essential" device.

Between the War Years
At the conclusion of the first world war the Sperry Gyroscope Company focused its attention on expanding its marine business involvement around the world. The Sperry Gyroscope company, and Elmer Sperry in particular, spent considerable effort appointing agents and representatives around the world. One of the first, established in 1918, was the Mitsubishi Zosen Kaisha Company (Mitsubishi Shipbuilding) of Japan, a company that was licensee for all products there. The first civil installation of the gyrocompass was aboard the luxury liner SS AQUITANIA of the Cunard Steam Ship Company (pictured here at the left in a company poster of the time - The AQUITANIA retired from service in 1949 with many Sperry products aboard). In 1922 field trials commenced on the Sperry standard Gyro Pilot. The first recorded crossing of the Atlantic with a ship under complete gyro pilot control is credited to the Standard Oil Company's Tanker W.H. TILFORD, under the command of Captain Alex Mackay. Captain Mackay, according to the record, initially had a very low opinion of "Iron Mike" but became a believer soon after the transit of the Atlantic had started.
In the closing days of 1928 Elmer Sperry, at the age of 68, sold the Sperry Gyroscope Company to the North American Aviation Company. On January 17th of 1929, the Sperry Gyroscope Company became a legally registered corporation in the State of New York. Thomas A. Morgan, one of the first two original employees at the formation of the company in 1911, was elected President and General Manager of the new company by its Board of Directors. The new company focused on the urgent requirement for an artificial horizon for aircraft. Working closely with Lt. James Doolittle, who had been assigned by the U.S. Army Air Corps to carry on the work, Sperry engineers quickly developed two new instruments which were soon being flight tested. These were the artificial horizon and the aircraft directional gyro. The test flight of these instruments on September 24, 1929 by Doolittle was the first recorded all blind flight in history. These two instruments immediately found their way aboard airmail planes and the aircraft of the fledgling commercial airlines (TWA was the first commercial buyer of these two products).
In 1933 North American Aviation reorganized is divisions and the Sperry Gyroscope Company Inc. became a subsidiary of the new Sperry Corporation. R.E. Gillmoor, the other first employee of the original company was elected its President.

During the period from the end of the First World War to that of the Second, Sperry Gyroscope produced a number of marine gyrocompass variants. These included the MK6, the MK8 and probably the most famous, the MK14. The MK14 emerged in 1933-4 and continued to be built well into the 1950's. The MK14 found its way aboard such famous ships as the QUEEN ELIZABETH 1, QUEEN MARY (shown above), the SAVANNAH (the first nuclear powered merchant ship), THE UNITED STATES (holder of the famous Blue Ribband - for fastest crossing of the Atlantic by a regular passenger ship) and the tanker MANHATTAN, which made the first Northwest Passage crossing. There are many MK14's still in service around the world today which testifies not only to its robustness, but to the quality of the basic design itself. The most significant technological event during this period was the introduction of the electronic amplifier to gyrocompasses. The use of electronics eventually found its way into all Sperry products.
The Second World War
With the outbreak of the Second World War Sperry suddenly found itself inundated with demands for gyrocompasses from all allied navies. Demand was so great that by the time of Pearl Harbor, Sperry Gyroscope had expanded its employee count in excess of five times and its production by ten times what they had been in 1936. With Sperry Gyroscope Ltd. in the U.K. in full production and the factory in New York also saturated with demands on its production line, Sperry allowed its now famous MK14 to be produced under license by Chrysler's Dodge Division. In 1943, the U.S. Government finalized contracts with the Chrysler Dodge for 5,500 units, as well as to the Package Machinery Company in Massachusetts. Throughout the war, Sperry and its subsidiary company in the U.K. produced gyrocompasses, compass repeaters, battery fire control systems, and related systems for the various allied nations as well as other instruments for aircraft. By war's end, some 22 companies were producing Sperry products under license for the allied war effort. From an employee count of 600 in 1932, Sperry grew to a wartime peak of 32,000 in 1943. Another 32,000 were subcontracted and when prime contractors were taken into account, over 100,000 people worked for Sperry Gyroscope at its peak employment period in 1943.
 USS Sperry USS Sperry
In recognition of Elmer A. Sperry's contribution to the people and government of the U.S., the U.S. Navy, on February 1, 1941, laid the keel for AS-12, the USS SPERRY (shown at left) at the Mare Island Naval Shipyard in California. On December 17, 1941, the USS SPERRY was launched and had the dubious distinction of being the first U.S. Naval combatant commissioned after the attack on Pearl Harbor. The USS SPERRY, a fleet Submarine Tender, served throughout the war, spending her entire time in the western Pacific. She served with distinction until 1982 and after 40 years of service was moved to Bremerton, Washington, where she sits today awaiting final disposition.
From World War to Peaceful Growth
Corporate Changes and New Owners
At the end of the war, the Sperry Corporation and its subsidiary, Gyroscope, saw great expansion. Much of this expansion was attributable to emerging electronics technologies. This expansion eventually led to the acquisition of the Remington Rand Corporation in 1955. At the completion of the acquisition, Sperry Corporation became the Sperry Rand Corporation and stayed with this name until 1979. At about the same time as the Rand acquisition, Sperry Gyroscope decided to open a facility that would almost exclusively produce its marine instruments. After considerable searching and evaluation, the Charlottesville area of Central Virginia was selected as the site. In 1956, Sperry Piedmont Division opened its doors for business.
Reorganizations within the Sperry Rand Corporation resulted in subsequent name changes and in 1967 the Piedmont Division name was dropped and replaced with the Marine Systems Division of the new Sperry Rand Electronics group.
MK37 and MK27
 During the period from 1956 to 1986, many now famous products were designed and built at the Sperry Marine Division. Among these were the MK37 (the new MK37VT, introduced in 1995, is shown at the right) commercial gyrocompass and its military equivalent, the MK27. Others included the MK19 Naval Attitude and Heading Reference System, the APN59 airborne weather radar and many others. Eventually, Sperry Marine's product mix would include over 60 different products for the military and commercial marine communities as well as the Air Force. It was also during this period that the U.S. Navy's THRESHER (SSN 593) sank with all hands aboard. The list of those who lost their lives also included two Sperry Marine Field Engineers: Kenneth R. Corcoran and Donald T. Stadtmuller. During the period from 1956 to 1986, many now famous products were designed and built at the Sperry Marine Division. Among these were the MK37 (the new MK37VT, introduced in 1995, is shown at the right) commercial gyrocompass and its military equivalent, the MK27. Others included the MK19 Naval Attitude and Heading Reference System, the APN59 airborne weather radar and many others. Eventually, Sperry Marine's product mix would include over 60 different products for the military and commercial marine communities as well as the Air Force. It was also during this period that the U.S. Navy's THRESHER (SSN 593) sank with all hands aboard. The list of those who lost their lives also included two Sperry Marine Field Engineers: Kenneth R. Corcoran and Donald T. Stadtmuller.
The Sperry and Burroughs Corporations merged to form UNISYS in 1986. This merger, and the subsequent focus that the new UNISYS placed on its core business segment, the computer market, sealed the fate of the Aerospace and Marine Group. Sale of the group was foreordained and the only task was to find a suitable buyer or buyers. As events unfolded, it became obvious that no single buyer would or could acquire the combined Group and the division of the two into separate assets made sense. Thus, Aerospace and Marine were separated and the bulk of the Aerospace business was subsequently purchased by Honeywell. Sperry Marine and its far flung international organization were acquired by Tenneco. These purchases were formalized in 1987 with day to day operation of Sperry Marine being taken over by Newport News, a substantial division of Tenneco, in the early months of 1988.
 MK49 MK49
In 1993 the J.F. Lehman investment group purchased Sperry Marine from Tenneco. In 1995, the U.S. Navy awarded a contract to Sperry Marine for the MK49 Ring Laser Gyrocompass Ship's Inertial Navigator (RLG SINS - Shown at left), subsequently called the WSN-7 SINS. The purpose of this program is to replace all existing older technology ballistic wheel and suspended gyro based navigators throughout the fleet in both surface and subsurface assets.
Litton
In early 1996, Litton made an offer to purchase Sperry Marine. In May, this offer was accepted. On May 15th, Sperry Marine became a part of the Litton Guidance and Controls Division.
Chronology of Northrop Grumman Sperry Marine Company History:
1910 - Formation of the Sperry Gyroscope Company by Elmer A. Sperry
1913 - Formation of the Sperry Gyroscope Limited Company in the U.K.
1928 - Sperry Gyroscope sold to North American Aviation
1929 - (January 17th) Incorporation - Sperry Gyroscope Company becomes Sperry Gyroscope Incorporated
1933 - North American Reorganizes divisions and forms Sperry Corporation. Sperry Gyroscope becomes subsidiary company to Sperry Corp.
1941 - USS SPERRY (AS-12) Launched
1955 - Acquisition of Remington Rand - Name Changes to Sperry Rand Corporation
1956 - Sperry Piedmont Company opens for operation in Charlottesville, Virginia
1967 - Sperry Piedmont changes name to Marine Systems Division of Sperry Rand Corporation
1979 - Sperry Rand changes to Sperry Corporation and Marine Systems Division becomes division of Sperry Corporation's Electronics Group
1982 - USS SPERRY Decommissioned
1984 - Reorganization places Marine Systems Division within the Aerospace and Marine Group
1986 - Merger with Burroughs forms UNISYS Corporation
1987 - Tenneco purchases Marine Systems Division and changes name to S-P Marine
1987 - S-P Marine renamed to Sperry Marine Inc.
1993 - Sperry Marine purchased from Tenneco/Newport News by John Lehman and Associates
1995 - (January) U.S. Navy purchases WSN-7, marking the introduction of marine RLG technology to the fleet.
1996 - (May) Litton concludes purchase of Sperry Marine from J.F. Lehman & Associates
2001 - Sperry Marine becomes part of the Northrop Grumman Corporation.
Additional Reading:
For additional information on Sperry and the history of the company, its technologies, gyrocompasses, and related material, the following is a very incomplete listing of publications that can be found:
1.) "The Theory of the Gyroscopic Compass" by A.L. Rawlings, The MacMillan Company, 1944
2.) "Elmer Sperry - Inventor and Engineer" by Thomas Parke Hughes, John Hopkins Press, 1971, ISBN o-8018-1133-3
3.) "Gyro! The Life and Times of Lawerance Sperry" by William Wyatt Davenport, Charles Scribner's Sons, New York, 1978
4.) "Sperry's Forty Years in the Progress of Science" by Preston R. Bassett, "Sperry Scope" Corporate Newsletter, 1950
|